Problem Areas
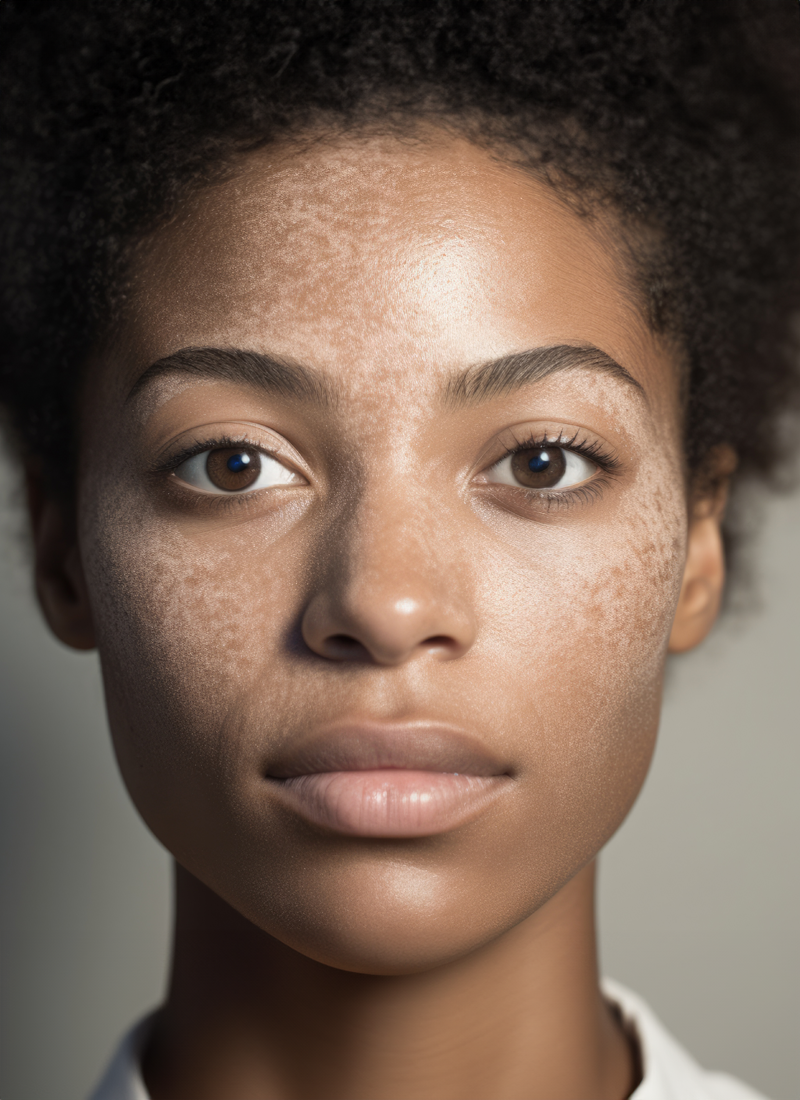
What Is Melasma?
Melasma is a common skin condition characterized by dark, discolored patches on the skin, often found on the face. These patches typically appear on the cheeks, forehead, nose, and upper lip, and are usually brown or gray-brown in color. Melasma is more common in women, especially during pregnancy or when taking hormonal contraceptives, but it can also affect men. It is often associated with sun exposure and hormonal changes.
Causes of Melasma
- Sun Exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) light from the sun can trigger melasma or worsen existing patches by stimulating melanin production in the skin.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones, such as during pregnancy (often referred to as the “mask of pregnancy”), or with the use of oral contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy, can contribute to melasma.
- Genetics: A family history of melasma may increase the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Skin Type: Individuals with darker skin tones are more prone to melasma due to higher levels of melanin production.
Potential Negative Outcomes If Left Untreated
- Cosmetic Concerns: Melasma can affect self-esteem and confidence due to the visible dark patches on the skin, which may be distressing for those affected.
- Progressive Darkening: Without treatment, melasma may worsen over time, with dark patches becoming more pronounced and widespread.
- Psychological Impact: Persistent melasma can lead to anxiety or stress related to appearance, potentially impacting overall mental health.
- Complications from Self-Treatment: Using inappropriate or harsh treatments without professional guidance can exacerbate melasma or cause further skin damage.
Best Treatments For Melasma
Treating melasma involves a combination of approaches to reduce pigmentation and prevent recurrence. Effective management can improve skin appearance and boost confidence.
Prescription creams containing ingredients such as hydroquinone, tretinoin, or corticosteroids can help lighten dark patches by inhibiting melanin production and promoting cell turnover.
Peels using glycolic acid or trichloroacetic acid (TCA) can help exfoliate the skin and reduce pigmentation by removing the outer layers of the skin.
Laser treatments like fractional lasers can target and break up melanin deposits in the skin, leading to a reduction in pigmentation.
Microneedling combined with topical treatments can improve melasma by enhancing product absorption and stimulating skin regeneration.
Daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF is crucial to protect the skin from UV damage and prevent melasma from worsening.