Problem Areas
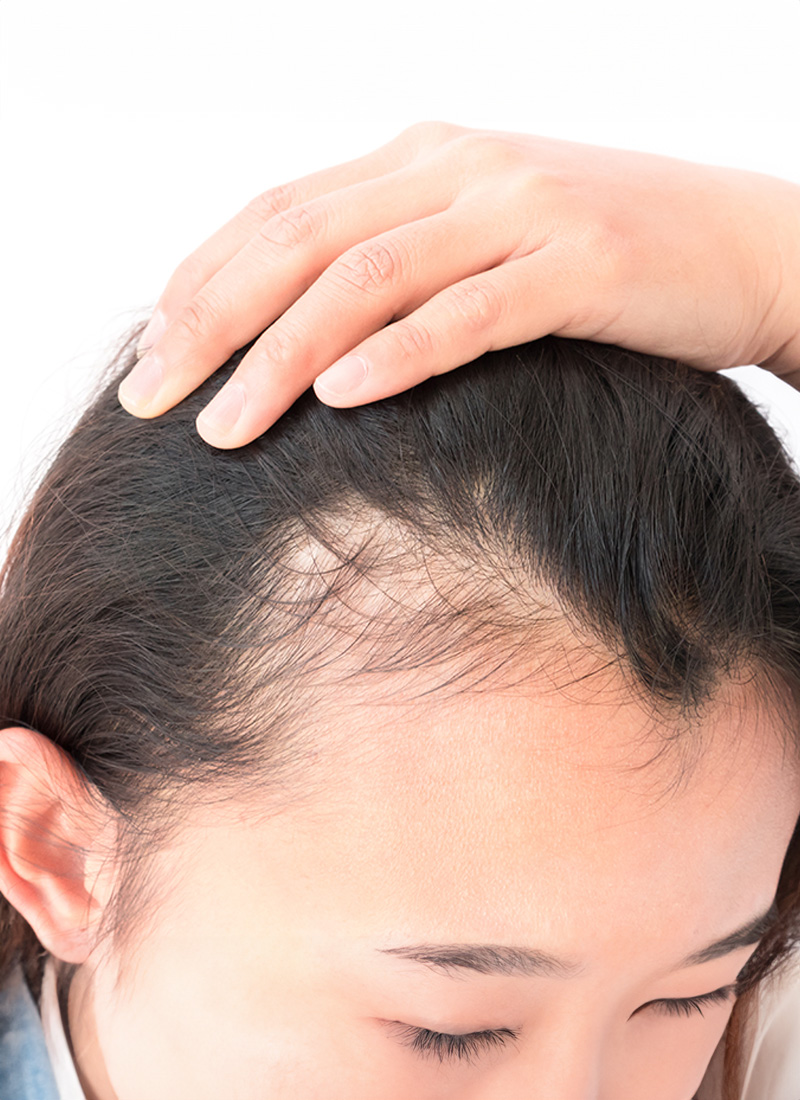
What Is Thinning Hair?
Thinning hair refers to a gradual decrease in hair density and volume, often resulting in a less full and more sparse appearance. This condition can affect both men and women and may start as early as the late teens or early twenties. Thinning hair can be a part of normal aging, but it can also be a sign of underlying health issues or genetic predisposition.
Causes of Thinning Hair
- Genetics: Genetic factors are a leading cause of thinning hair, with conditions such as androgenetic alopecia (male or female pattern baldness) being hereditary.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal imbalances due to conditions like thyroid disorders, pregnancy, or menopause can contribute to hair thinning.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of essential nutrients, such as iron, vitamin D, or biotin, can negatively impact hair health and lead to thinning.
- Stress: High levels of stress can trigger hair loss conditions like telogen effluvium, which leads to temporary thinning of the hair.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, including autoimmune diseases and scalp infections, can cause thinning hair.
- Medications: Some medications, including those for cancer, arthritis, and hypertension, may have side effects that include hair thinning.
Potential Negative Outcomes If Left Untreated
- Increased Hair Loss: Without intervention, thinning hair may progress to more significant hair loss or baldness.
- Reduced Self-Esteem: Thinning hair can impact self-image and confidence, leading to emotional distress.
- Psychological Impact: Persistent hair thinning can cause anxiety or depression related to appearance and self-worth.
- Potential for Permanent Hair Loss: Addressing thinning hair early can prevent more severe hair loss and potential permanent baldness.
Best Treatments For Thinning Hair
Treating thinning hair effectively involves addressing the underlying causes and utilizing various treatments to promote hair growth and restore hair density. Early and appropriate treatment can help manage thinning hair and improve overall hair health.
Products like minoxidil (Rogaine) can stimulate hair growth and slow down hair loss by improving blood flow to the scalp.
Prescription medications, such as finasteride (Propecia), can help reduce hair loss and promote regrowth by addressing hormonal imbalances.
PRP therapy involves injecting concentrated platelets from the patient’s own blood into the scalp to stimulate hair follicles and encourage hair growth.
Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) can improve hair density and growth by increasing blood flow and stimulating hair follicles.
Surgical options, such as follicular unit transplantation (FUT) or follicular unit extraction (FUE), can relocate healthy hair follicles to areas of thinning or baldness for a more permanent solution.